Nematodes
Scientific Name
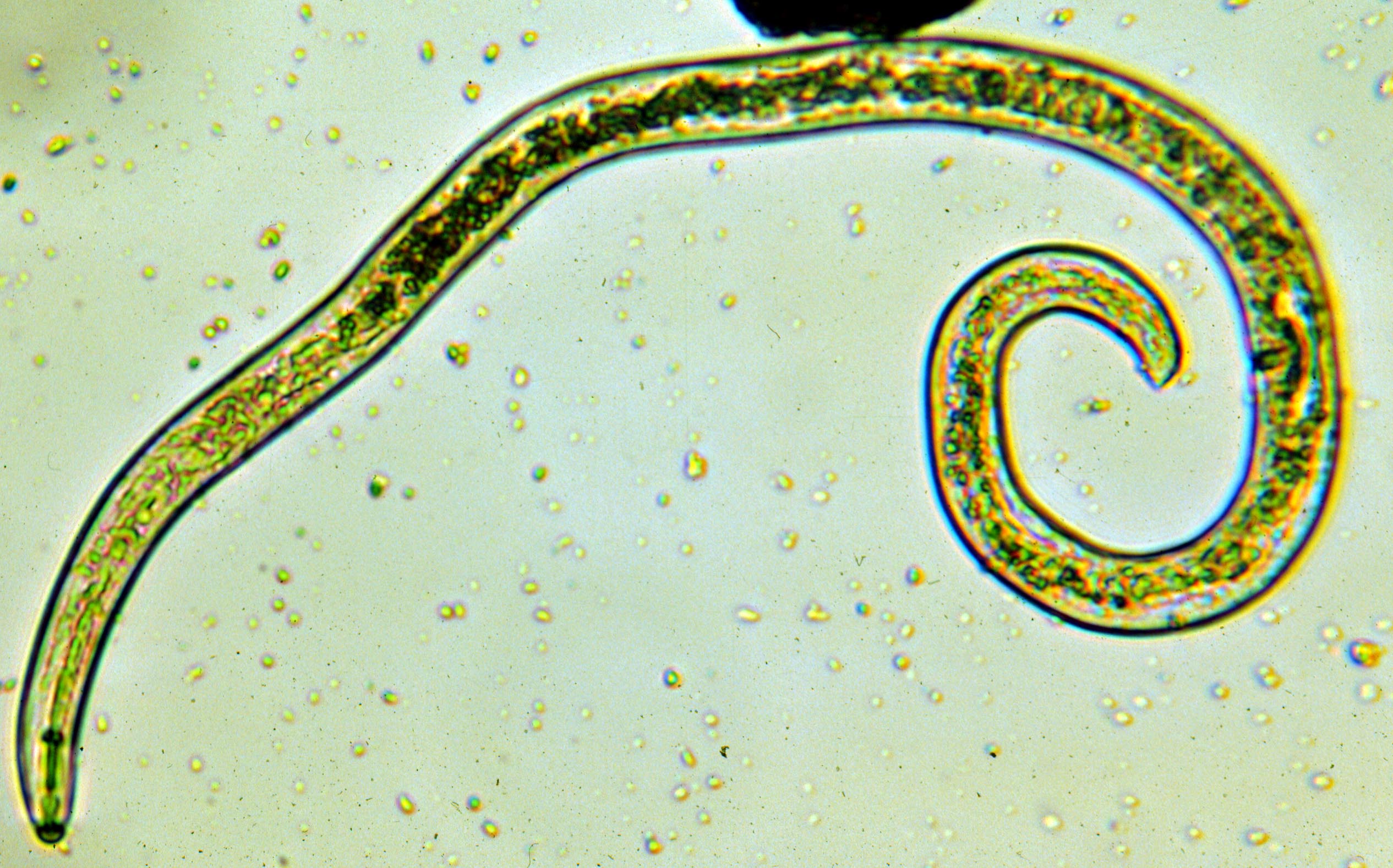
Meloidogyne spp.
Description
Nematodes are microscopic roundworms that attack plant roots, causing the formation of galls and disrupted nutrient uptake. Infested plants typically display stunted growth and wilting.
Characteristics
Though invisible to the naked eye, their damage is evident through swollen, knotted roots and overall decline in plant vigor. They interfere with water and nutrient absorption, significantly weakening the host plant.
Control Methods
- Organic sprays: Apply neem-based products or compost teas as bio-nematicides to suppress harmful nematode activity.
- Cultural practices: Enhance soil organic matter with compost and maintain balanced soil pH to create unfavorable conditions for nematode proliferation.
- Preventive methods: Utilize crop rotation with non-host plants and practice rigorous soil management to minimize nematode populations.
- Biological controls: Introduce beneficial nematodes and soil microbes that outcompete or prey on harmful nematodes.
- Mechanical physical: Employ soil solarization in warm climates and implement strict sanitation to prevent the spread of nematodes.
Natural Enemies
- Beneficial Nematodes
- Soil Microbes
- Predatory Fungi